
In today’s data-driven world, Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a powerful tool that simplifies data collection and allows marketers to track user behavior, set up analytics tags, and automate complex data collection processes. This article explores GTM’s key features and best practices for effective data management.
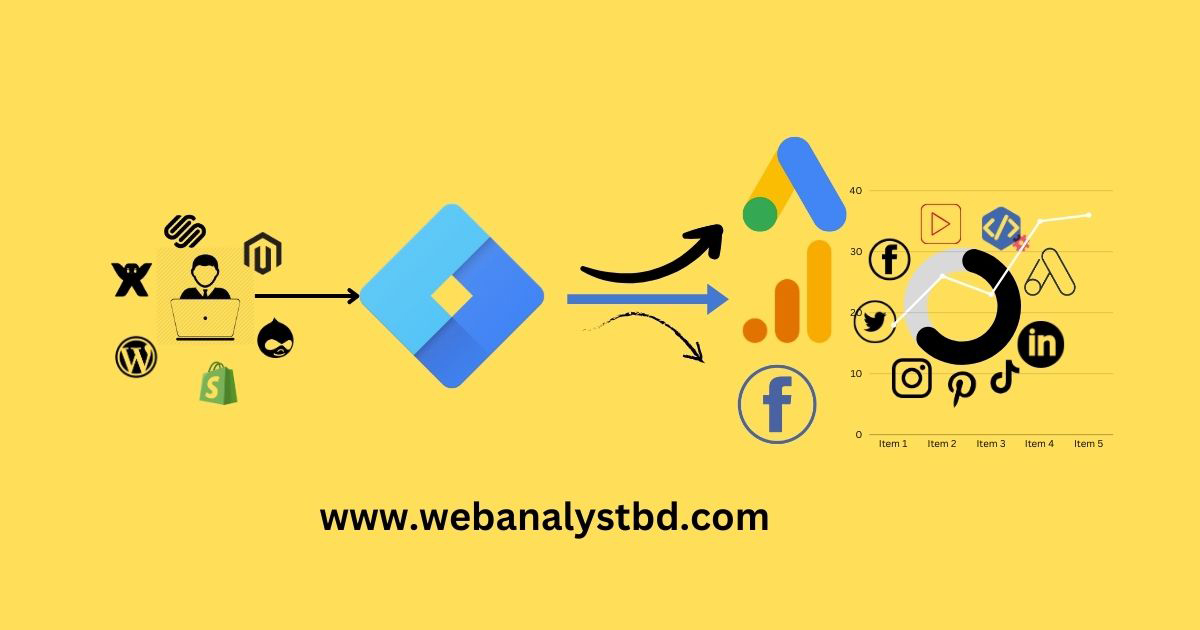
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a free tool for adding and managing various tracking tags on your website or app without having to update code manually. Tags are snippets of code or tracking pixels used to collect data on user interactions, conversions, and other key behaviors. GTM enables marketers, developers, and data analysts to control all tags, triggers, and variables in a central interface.

GTM offers several benefits for data management, including:
While GTM and Google Analytics are complementary, they serve distinct roles. GTM manages tags and tracks events on your website or app, while Google Analytics organizes, visualizes, and reports on the data collected by GTM. Together, they form a robust analytics system, but they operate separately in data collection and visualization.
To get started with GTM, follow these steps:
GTM Setup for Specific Platforms
For platforms like WordPress and Shopify, you can use GTM plugins or manually insert code into the site’s theme files.
Here’s a simple overview of setting up tags, triggers, and variables:
Define Variables: Use variables to store dynamic data like Page Path or Click Text, enhancing the precision of your tags and triggers.
Tags are snippets of code used to track user actions, conversions, page views, and other metrics. They can be configured to send data to Google Analytics, Facebook, LinkedIn, Pinterest, Twitter, Instagram and more.
Triggers determine when a tag should fire. Each trigger sets conditions (like page load or click) that must be met before a tag is executed, ensuring precise data collection.
Variables in GTM store dynamic values that tags and triggers use. These values could be Page URLs, Click Texts, or specific identifiers for custom tracking needs.
The Data Layer acts as a space for storing user interaction data, which can be accessed by tags, triggers, and variables. It allows for complex tracking like eCommerce details or user preferences, minimizing manual code changes.
With evolving privacy regulations, Consent Mode allows GTM to adjust tracking behavior based on user consent. This is essential for compliance with GDPR and other privacy laws.
Preview and Debugging Mode lets you test tags, triggers, and variables before deployment, helping to ensure data accuracy by showing which tags fire and under what conditions.
Custom templates offer pre-configured tag and variable setups for standardized tracking across sites or GTM containers, making it easier to manage and maintain consistent data.
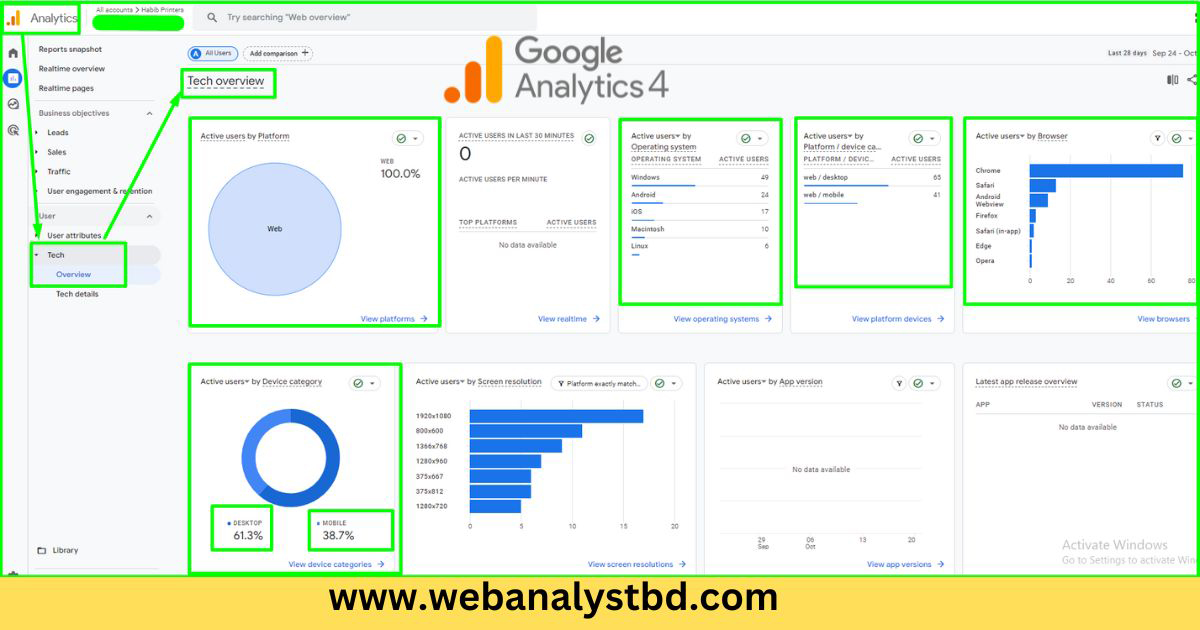
Enhanced Measurement in GTM automates tracking of standard events (e.g., page views, scroll depth, file downloads) without requiring extensive coding, making it accessible for sites lacking developer resources.
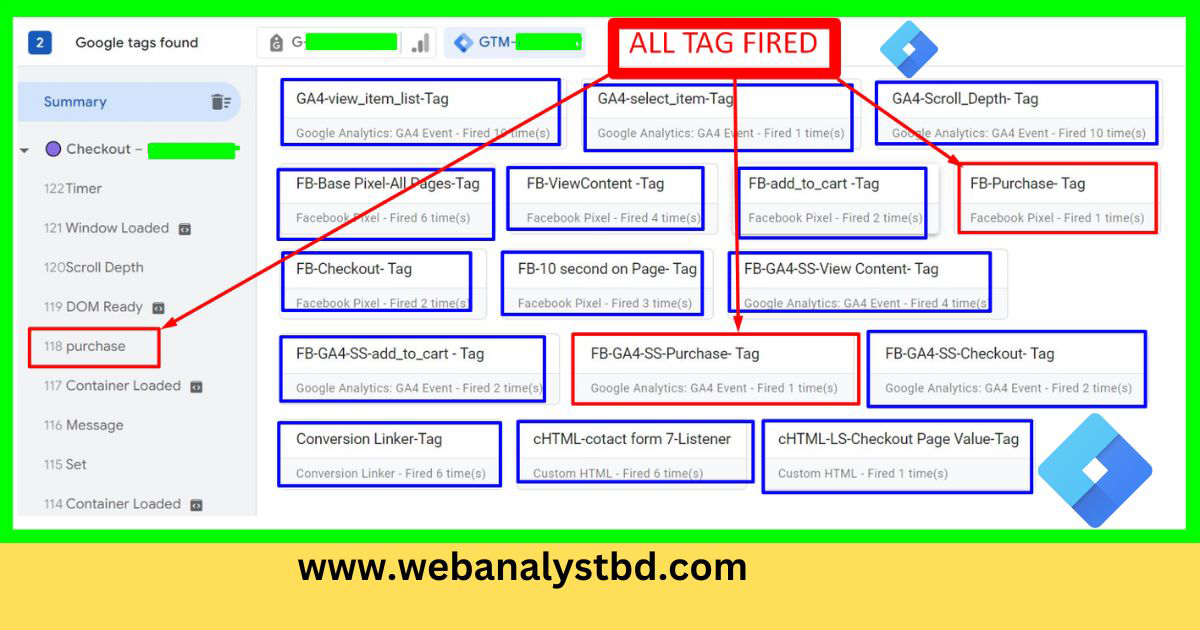
Use Preview Mode to troubleshoot common GTM issues:
For advanced GTM setups, consider:
GTM is a free tool for adding and managing tracking tags (like analytics pixels) on websites or apps without code changes, centralizing tag, trigger, and variable management.
GTM handles tag management and event tracking, while Google Analytics analyzes and reports the data.
Tags are snippets of code that track user actions on your site, such as clicks, form submissions, or conversions. They send data to tools like Google Analytics or advertising platforms, providing valuable insights for optimizing marketing strategies and user experiences.
Triggers determine when tags should be fired. For instance, a trigger can be set for a page load, button click, or form submission. By defining triggers, you can precisely control when and where data is collected, improving data accuracy and relevance.
The Data Layer is a JavaScript object that holds detailed information about user interactions and site data. GTM uses the Data Layer to track complex data like eCommerce details or user preferences, ensuring flexibility in data management and reducing the need for hard-coded tracking.
Variables store dynamic data that tags and triggers use to enhance tracking precision. GTM offers built-in variables (like Page URL and Click Text) and allows custom variables for specific data points, making it easier to track particular events or actions.
To start with GTM, create an account and a container for your website or app, then install the GTM code on your site. From there, you can add tags, set up triggers, and define variables to start collecting data.
Consent Mode allows GTM to adjust data collection based on user consent preferences, helping businesses comply with regulations like GDPR. When users opt out of certain tracking, Consent Mode modifies data collection, ensuring both compliance and data continuity.
GTM’s Preview and Debugging Mode is designed for troubleshooting. It allows you to see which tags are firing, inspect triggers and variables, and identify potential issues in real-time before publishing any changes live.
Enhanced Measurement, primarily for Google Analytics 4 (GA4), enables automated tracking of key events, like page views and scrolls, without requiring custom coding. This feature makes it easier for sites without developer resources to set up and maintain tracking.
GTM allows marketers to manage and implement tags independently, reducing dependency on developers. This streamlines workflows and ensures quicker updates and tracking adjustments.
Yes, GTM offers community templates for common tracking setups (e.g., Facebook Pixel, LinkedIn Insight). You can also create custom templates to address unique tracking needs, simplifying tag management across multiple GTM containers or websites.
To ensure data accuracy, regularly test tags in Preview Mode before publishing, document all configurations, and use clear naming conventions for tags, triggers, and variables. Additionally, make use of GTM’s version control to revert to previous setups if needed.
GTM centralizes tag management, enhances data accuracy, and offers flexibility for tracking various user actions. Its integration capabilities, especially with GA4, make it a powerful tool for managing and optimizing data collection without the need for complex code changes.

GTM provides an efficient and accurate way to manage data, optimizing your tracking and analytics setup. By implementing tags, triggers, variables, and advanced features like the Data Layer and Consent Mode, GTM can create a streamlined data environment that supports your business objectives and compliance requirements.
At Web Analyst, our team is here to support you with GTM and GA4 setups, as well as troubleshooting services to enhance your digital strategy and ensure data accuracy.
Contact Web Analyst today for expert guidance on optimizing your data management and analytics strategy and tracking solutions.

Written by Md. Anwar Hossain – Web Analyst


















